|
|||||

|

|
|

|

|
|
On the sum ∑ ⟨nα⟩−t and
numerical integration
Seymour Haber and Charles Freeman Osgood |
|
Vol. 31 (1969), No. 2, 383–394
|
Abstract |
|
Let “⟨x⟩” denote the distance of the real number x from the nearest integer. If α is an irrational number, the growth of the sum 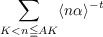 (A is a fixed number, > 1) as K →∞ depends on the nature of the rational approximations to α. We shall find estimates of this sum, for certain classes of irrational numbers. Part of the motivation for these estimates is an application to Korobov’s theory of numerical evaluation of multiple integrals. |
Mathematical Subject Classification
Primary: 65.55
|
Milestones
Received: 12 December 1968
Published: 1 November 1969
|
Authors |
| Seymour Haber | |
| Charles Freeman Osgood | |
 |
