|
|||||

|

|
|

|

|
|
On the asymptotic
behavior of solutions of x′′
+ a(t)f(x) =
e(t)
Theodore Allen Burton and Ronald Calvin Grimmer |
|
Vol. 41 (1972), No. 1, 43–55
|
Abstract |
|
In this paper sufficient conditions are given which insure that all solutions of 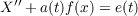 tend to zero as t →∞. Results obtained are comparable to those obtained for the linear equations via two Liouville transformations. Also, related results concerning stability and boundedness of solutions and, when e(t) = 0, necessary and sufficient conditions for the uniqueness of the zero solution on an interval where a(t) is negative are given. |
Mathematical Subject Classification 2000
Primary: 34D05
|
Milestones
Received: 30 April 1971
Published: 1 April 1972
|
Authors |
| Theodore Allen Burton | |
| Ronald Calvin Grimmer | |
 |
